The Indian pharmaceutical industry is a globally significant sector, valued at approximately USD 50 billion in FY 2023–24. It is projected to grow to USD 130 billion by 2030, with potential to reach USD 450 billion by 2047. Known as the “Pharmacy of the World,” India possesses the third-largest pharmaceutical sector in terms of volume.
Pharmaceutical careers are highly sought after by graduates in B. Pharm, M. Pharm, and other life science disciplines. However, many job seekers find it challenging to navigate the vast landscape of opportunities within the industry. This guideline aims to provide a clear overview of the available roles and help aspiring professionals make informed career decisions.
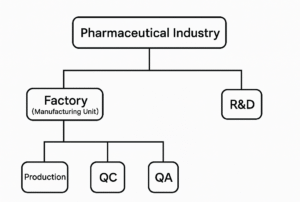
Jobs in the pharmaceutical industry can broadly be classified into two major domains: (1) Manufacturing Site-Based Roles (Factory Premises) and (2) Research and Development (R&D) Roles. Each of these is further subdivided into specialized departments, often with interdependent functions.
- Factory Premises Roles
These roles are typically based at manufacturing sites and are divided into the following core departments:
- Production: Production is the central operation of any pharmaceutical manufacturing unit. It involves the transformation of raw materials into finished pharmaceutical products using standardized machinery and procedures. The department strictly adheres to safety and sterility protocols, requiring the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and gowning practices. Production may be subdivided into specific process stages, including Mixing, Granulation, Compression, Coating, and Packaging. Each stage plays a crucial role in the overall production of dosage forms (tablets, capsules, etc.).
- Quality Control (QC): The Quality Control department is responsible for verifying the quality of materials and finished pharmaceutical products. It operates independently of the production line to ensure unbiased testing and compliance with regulatory standards. QC is further divided into Raw Material Testing (evaluation of materials upon receipt), Finished Product Testing (assessment of packaged batches before market release), Stability Studies (monitoring product quality over time), and GLP (Good Laboratory Practices), which includes oversight of instruments such as HPLC, FTIR, UV spectroscopy, and analytical balances.
- Quality Assurance (QA): The QA department ensures adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). It oversees both QC and Production departments to confirm that all processes meet defined quality standards. Subsections within QA include Analytical Quality Assurance (AQA), which focuses specifically on the quality of analytical work done in the QC lab.
- Research & Development (R&D)
R&D centers are the innovation hubs of pharmaceutical companies. They are responsible for the development of new drug formulations, optimization of manufacturing processes, analytical method validation, and ensuring regulatory compliance for product registration. Due to the technical expertise required, R&D positions generally demand at least an M. Pharm or equivalent qualification in pharmaceutical sciences or chemistry.
What Should You Choose?
With so many roles available, it is natural for a fresh graduate to feel uncertain. It is important to note that pharmaceutical careers are often specialized, and switching between domains later can be difficult. Therefore, assess your interests and long-term goals carefully before choosing a career path in Production, Quality Control, Quality Assurance, or Research & Development.
